Connections
During development, we may want to use different connections to test our DAGs. Also, for the same connections we might want different details per environment.
For example, we may start development writing to a local file and after that is working correctly switch the connection to S3 to finish testing. Finally we want to move this to the production S3 bucket in a seamless way.
- data_lake workflow
- local -> disk
- dev -> dev S3 bucket
- prod -> production S3 bucket
For this specific purpose there is a file called connections.yml. This is where we will define all our connection details for our project for all environments.
Connections YAML
For example in this project we will write data using a connection called data_lake which has two connection environments, local which writes to a local file and test which writes to S3. It is possible to use them interchangeably since they both implement the same interface: FileSystemHook.
connections.yml:
data_lake:
local:
conn_type: local_storage
extra:
base_path: /tmp/data_lake/
test:
conn_type: s3
extra:
bucket: my-typhoon-test-bucket
connections.yml is not versioned
The connections.yml file may contain passwords so it should never be versioned. That is why it's included in the .gitignore file for projects generated with the CLI.
Adding the connection
Following the advice we got from the typhoon status command we will now add the connection to the metadata database. We will add the local data_lake connection with the command:
typhoon connection add --conn-id data_lake --conn-env local
# Check that it was added
typhoon connection ls -l
# add the echo one too for completeness
typhoon connection add --conn-id echo --conn-env local
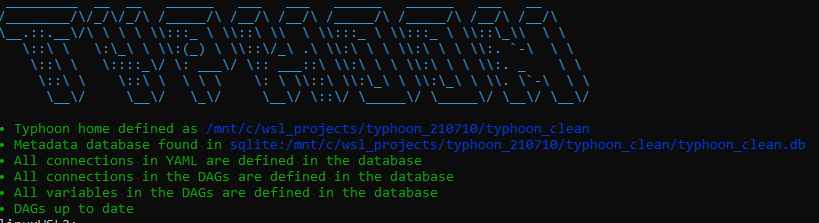
If we run the status command again we will see that everything is ok in our project now:
typhoon status
Connections types (Hooks)
Typhoon hooks represent the same thing as airlflow hooks, so if you are familiar it's an easy concept. They are the interface to external platforms and databases. You use the connections.yml to choose which hook to use and configure it. You can extend typhoon to connect to new platforms by adding Hooks. It comes with many popular ones already.
Hooks available:
- File System - local, S3, GC storage, Ftp
- DB API - most DBs can use this, e.g. MySql, MSSQL, Postgres, Redshift
- Snowflake specific flavour = SQLAlchemy - most DBs can use this
- AWS - AWS Session, DynamoDB
- Singer - You can use any singer taps in your DAG as a task. singer can connect to
Any you can add/extend your own, of course.